
Global Poverty Trends: Progress on Reducing Extreme Poverty (SDG 1)
The fight against extreme poverty has been a cornerstone of global development efforts, encapsulated in Sustainable Development Goal 1 (SDG 1): “End poverty in all its forms everywhere.” Over the years, significant progress has been made, but challenges remain as the world strives to meet the 2030 target.
Progress Achieved
- Decline in Extreme Poverty Rates: Since 1990, the global rate of extreme poverty—defined as living on less than $2.15 per day—has decreased dramatically. In 1990, nearly 36% of the world’s population lived in extreme poverty. By 2015, this figure had fallen to around 10%, showcasing the impact of coordinated global efforts.
- Regional Success Stories: Regions like East Asia and the Pacific have seen remarkable reductions in poverty, driven by economic growth, investments in education, and improved access to healthcare. For example, China alone lifted over 800 million people out of extreme poverty between 1981 and 2015.
- Policy and Programmatic Interventions: Social protection programs, microfinance initiatives, and investments in infrastructure have played a pivotal role in reducing poverty. Countries that have implemented targeted poverty alleviation strategies have seen significant improvements in living standards.
Challenges Ahead
- Impact of COVID-19: The pandemic reversed years of progress, pushing millions back into extreme poverty due to job losses, economic slowdowns, and disruptions in essential services. The World Bank estimates that global poverty increased for the first time in over two decades in 2020.
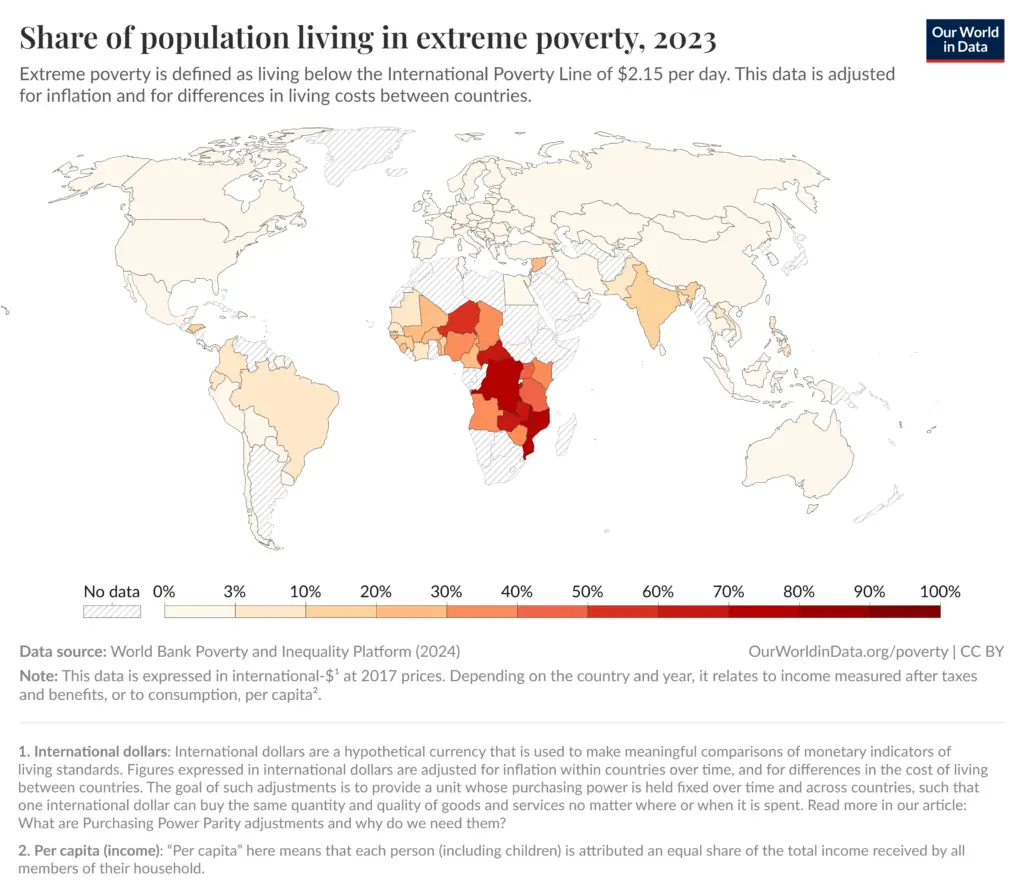
- Geographic Disparities: Sub-Saharan Africa remains a region of concern, with over 40% of its population still living in extreme poverty. Conflict, climate change, and limited access to resources continue to hinder progress in these areas.
- Multidimensional Poverty: Beyond income, poverty encompasses lack of access to education, healthcare, and basic services. Addressing these dimensions is critical to achieving SDG 1.
The Path Forward
To accelerate progress toward eradicating extreme poverty, a multi-faceted approach is essential:
- Strengthening Social Protection Systems: Expanding access to safety nets can shield vulnerable populations from economic shocks.
- Investing in Education and Skills Development: Equipping individuals with the tools to participate in the economy is key to breaking the cycle of poverty.
- Fostering Inclusive Economic Growth: Policies that promote equitable growth and job creation can uplift entire communities.
- Addressing Climate Change: Mitigating the effects of climate change is crucial, as it disproportionately affects the poorest populations.
While the journey to ending extreme poverty is fraught with challenges, the progress achieved thus far demonstrates that change is possible with sustained effort and global collaboration. By prioritizing inclusive and sustainable development, the world can move closer to realizing the vision of SDG 1.
Our World in Data team (2023) – “End poverty in all its forms everywhere” Published online at OurWorldinData.org. Retrieved from: ‘https://ourworldindata.org/sdgs/no-poverty’ [Online Resource]
You may also like




